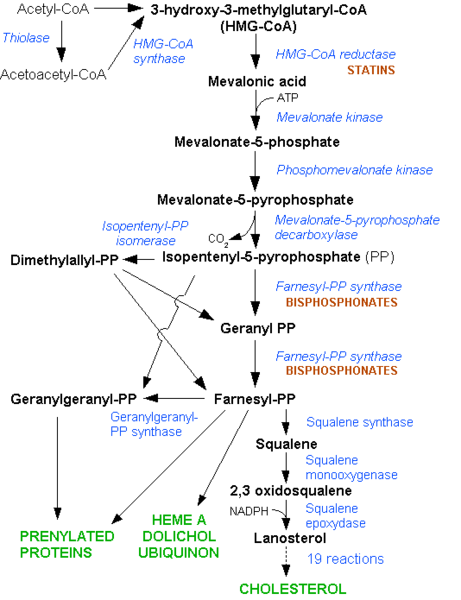
 Diagram of the Mevalonate Pathway
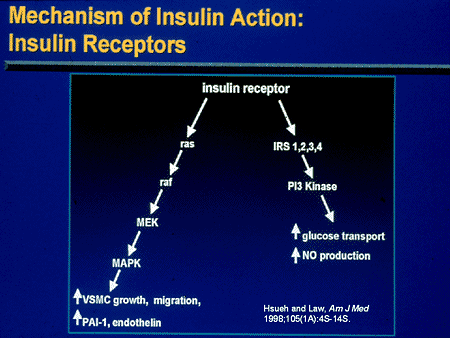 Schematic Diagram of Insulin Signal Transduction
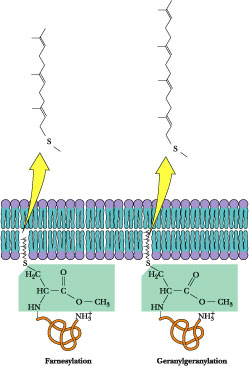 Diagram of Farnesylation & Geranylation of a Membrane Protein
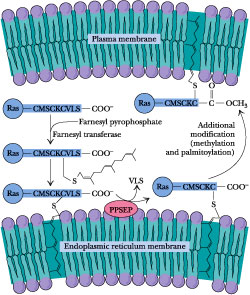 Prenylation of Ras (GTPase Protein)
| The Cholesterol Biosynthetic Pathway is central to the regulation of Cholesterol in serum
The rate-limiting step in Cholesterol Biosynthesis is Catalysed by the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase. This enzyme is the target of the Anti-hypercholesterolemic class of drug chemically described as statins.
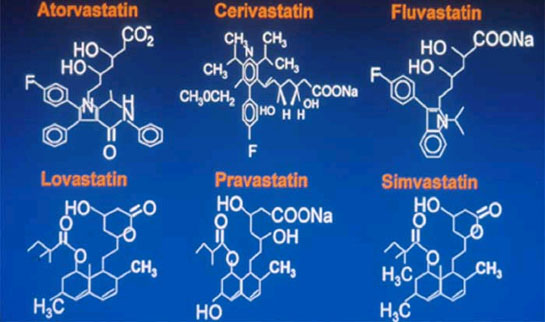 The first Natural statin was isolated by Japanese Researchers in the early 70's as efforts were being made to discovery inhibitors of HMG-COA reductase. It was proposed that Microorganism may produce inhibitors to this enzyme as a method of defense against other microorganisms.
It was also discovered that Mevalonate was a major precursor in the synthesis of egrosterol, an essential plant sterol. The first Natural statin was isolated from the Aspergillus terreus mold in 1976 by Merek & co it was commercially called Lovastatin.
The Mevalonate Pathway represents a target for Statins and Squalene synthase Inhibitors.
Insulin: Insulin ,the hormone, acts as a secondary messenger protein for a host of biochemical activities in the cell. This is achieved because Insulin acts as a surface ligand in the activation of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in the memebrane of the Target cells. Statins and Insulin Resistant: The proposed Theory insulin leads to the activation and translocation of GLUT-4 receptors in reponse to increased blood glucose. This occurs via a signal transduction mechanism which involves the activation of several proteins. The Insulin receptor substrate is a Protein whose activity depends upon the signal transmitted by the binding of Insulin to the initial cell-membrane Insulin receptor. This IRS protein further activates PI3 Kinase which in turn leads to the activation of proteins involved in the translocation of GLUT-4 receptors from the Golgi to the surface of the cell. Binding of IRS to the cell-membrane, to facilitate signal transduction, requires the action of prenyl proteins or the IRS protein, itself, may undergo Prenylation. Several other proteins undergo Prenylation including Ras (GTPASe) protein. Statins, by virtue of their activity on HMG-COA reductase effectively reduce cellular concentrations of Farnesyl Pyrophosphate and Geranyl Pyrophosphate two key precursors of the prenylation process. It is postulated that statins may contribute to insulin resistance over time by affecting the signal transduction pathway of insulin. Since the anchoring of IRS and RAS protein can, in theory, be affected by defects in the rate of prenylation. This proposed side-effect of statins can explain the potential anti-cancer effects that statins may exhibit when investigations are carried out. Statins: The Root of Metabolic Evil The mevalonate pathway is a critically important pathway in human cells. Several biomolecules can be created using intermediates of this pathway. These Include: steroid hormones, Vitamin D, Coenzyme Q10 (Ubiquinone),Heme A Prosthetic ( a compound of cytochrome a), and several other non-steroidial Isoprenoids. Therefore it can be deduced that statins can adversely affect processes such as: electron transfer (in Oxidative Phosphorylation) or Signal Tranduction cacade mechanisms. Not to mention the biosynthesis of essential steroid hormones.
|